The thyroid gland may be small, but it plays a big role in how your body functions. Located at the base of the neck, the thyroid is responsible for producing hormones that influence nearly every organ system in the body. From how fast your heart beats to how well your digestive system works, the thyroid’s impact is far-reaching. Among its most vital roles is regulating your energy, metabolism, and mood—three pillars of your everyday well-being.
When thyroid function is off, the effects can be profound. Let’s explore how this powerful gland affects energy levels, metabolic processes, and emotional health, and what you can do if you suspect a thyroid imbalance.
1. The Thyroid and Energy Levels
Thyroid hormones—primarily T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine)—play a crucial role in cellular energy production. These hormones help regulate how your body converts food into energy. When thyroid function is optimal, you generally feel alert, energized, and able to maintain normal activity levels.
However, when thyroid hormone levels drop (a condition known as hypothyroidism), your cells don’t get enough stimulation to produce adequate energy. This can lead to persistent fatigue, sluggishness, and a sense of being “run down,” even after a good night’s sleep. Everyday tasks may start to feel exhausting, and motivation tends to plummet.
Conversely, hyperthyroidism—an overactive thyroid—can cause the opposite problem. Too much thyroid hormone can lead to restlessness, difficulty sleeping, and nervous energy. While this might sound like an energy boost, the quality of that energy is usually erratic and unsustainable, often leading to burnout or anxiety.
2. Metabolism: The Thyroid’s Role as the Body’s Thermostat
Your metabolism determines how efficiently your body burns calories, and the thyroid is a major regulator of this process. When functioning correctly, it helps maintain a steady metabolic rate, allowing your body to use nutrients efficiently and maintain a healthy weight.
In hypothyroidism, metabolism slows down. This can result in unexplained weight gain, increased sensitivity to cold, constipation, and difficulty losing weight—even with regular diet and exercise. The body essentially enters a conservation mode, using energy more slowly than usual.
In contrast, hyperthyroidism speeds up metabolic functions. This can cause unintended weight loss, frequent bowel movements, and heat intolerance. While a faster metabolism might seem desirable, it often comes at the cost of nutrient depletion, muscle loss, and cardiovascular strain. A disrupted metabolism doesn’t just affect weight—it impacts everything from hormone balance to cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health.
3. Thyroid Function and Mood
Perhaps one of the most overlooked aspects of thyroid health is its impact on mood. Thyroid hormones directly influence brain chemistry, including the levels of serotonin and dopamine—neurotransmitters that regulate mood, motivation, and emotional stability.
Hypothyroidism is commonly associated with depression, brain fog, irritability, and lack of motivation. People often describe a “mental cloud” or a general sense of detachment or sadness. These symptoms can be easily mistaken for primary mood disorders, but when caused by thyroid dysfunction, they usually improve with proper treatment.
On the other end of the spectrum, hyperthyroidism can lead to anxiety, irritability, mood swings, and even panic attacks. The overstimulation of the nervous system creates a state of heightened alertness that may interfere with sleep and emotional regulation.
Because thyroid dysfunction can mimic mental health disorders, it’s crucial for individuals experiencing mood changes—especially when paired with physical symptoms like fatigue or weight changes—to have their thyroid checked as part of a comprehensive health evaluation.
What to Do If You Suspect a Thyroid Imbalance
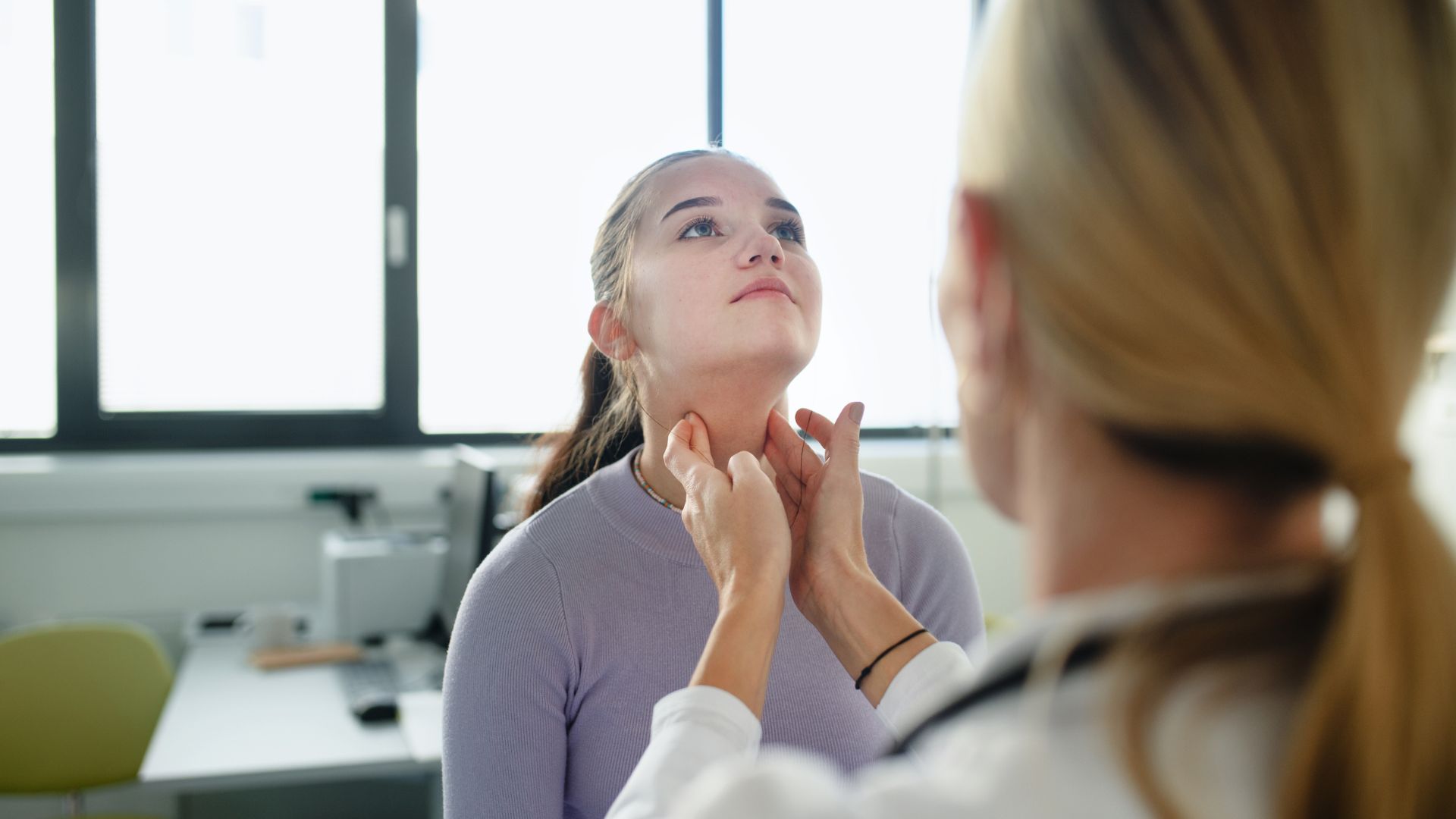
If you’re experiencing persistent changes in energy, metabolism, or mood, it’s important not to ignore them. Ask your healthcare provider for a thyroid function test, which typically includes measuring levels of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), Free T4, and sometimes Free T3.
Additional signs of thyroid imbalance can include:
- Dry skin or thinning hair
- Menstrual irregularities
- Heart palpitations
- Sensitivity to cold or heat
- Hoarseness or swelling at the base of the neck
Thyroid conditions are treatable. Hypothyroidism is often managed with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement (like levothyroxine), while hyperthyroidism may require medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
Final Thoughts
Your thyroid is a tiny gland with a massive influence on your physical and emotional health. If you’ve been feeling “off” and can’t explain why—whether it’s fatigue, unexpected weight changes, or emotional fluctuations—it’s worth exploring your thyroid health. A simple blood test could uncover a hidden issue and put you on the path to better energy, a balanced metabolism, and improved mood.
Understanding how the thyroid works empowers you to take control of your wellness—and feel more like yourself again.
If you are in the Pickering region and are interested in more naturopathic remedies, contact Dr. Cecilia Ho today. Call Dr. Cecilia Ho at 905-492-8688 to learn more!